 Present Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules, Usage" width="1068" height="601" />
Present Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules, Usage" width="1068" height="601" /> Present Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules, Usage" width="1068" height="601" />
Present Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules, Usage" width="1068" height="601" />
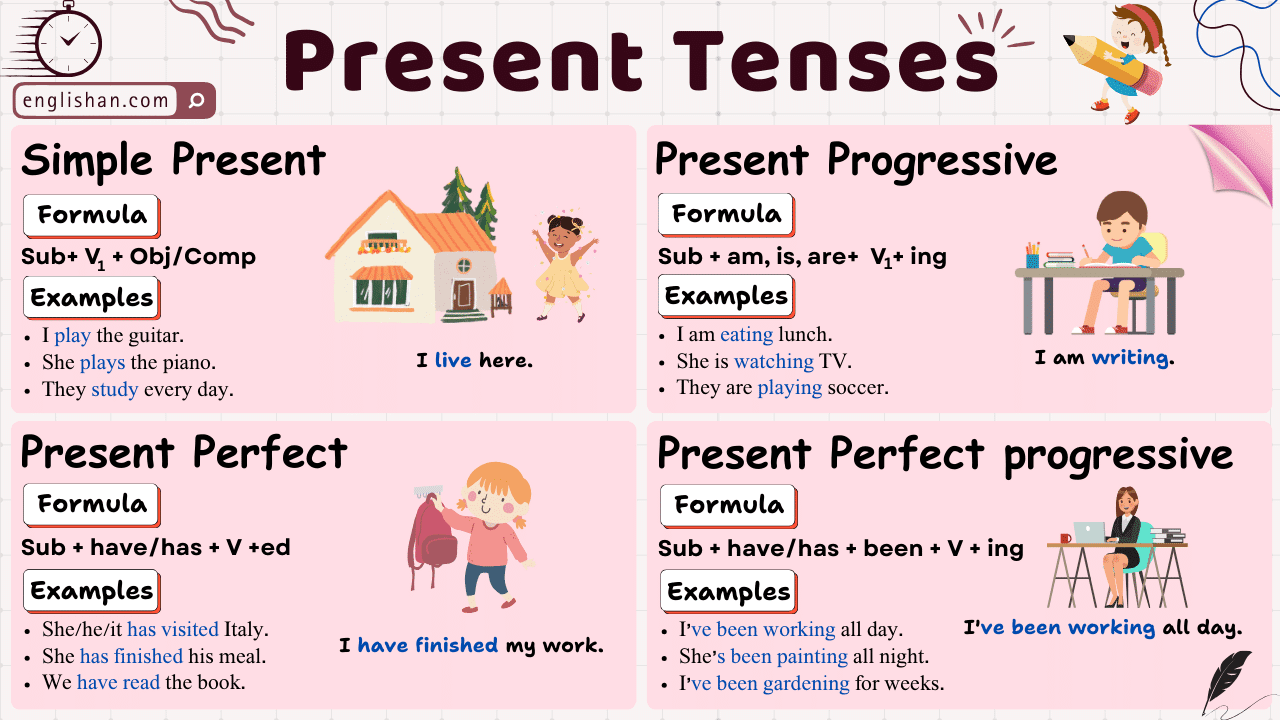
Throughout this section of the course, you’ll gain comprehensive insights into the English present tense. The present tense in English comprises the following:
In this article, we’re going to learn about all the types of present tense. You’ll get a clear idea of when and how to use each one. There are also exercises to help you practice and understand these tenses better.
Tenses in grammar indicate the time of an action. There are three main types: past, present, and future.
| Present | Past | Future | |
| Simple | I watch TV every evening. | I watched TV yesterday. | I will watch TV tomorrow. |
| Continuous | I am watching TV right now. | I was watching TV when the phone rang. | I will be watching TV at 8 PM tomorrow. |
| Perfect | I have watched TV already today. | I had watched TV before bedtime. | I will have watched TV by 9 PM. |
| Perfect Continuous | I have been watching TV for an hour. | I had been watching TV for two hours when you called. | By 10 PM tomorrow, I will have been watching TV for three hours. |
The present tense is a verb tense used to express an action or a state of being that is occurring in the present. It is often used to describe habits, routines, general truths, or states that are consistently true. In English, the present tense is typically formed by using the base form of the verb, with no additional inflections or auxiliary verbs for the singular subjects (I, you, he, she, it) and the plural subjects (we, you, they).
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I play soccer. | I do not play soccer. | Do I play soccer? |
| You | You play soccer. | You do not play soccer. | Do you play soccer? |
| We | We play soccer. | We do not play soccer. | Do we play soccer? |
| They | They play soccer. | They do not play soccer. | Do they play soccer? |
| He | He plays soccer. | He does not play soccer. | Does he play soccer? |
| She | She plays soccer. | She does not play soccer. | Does she play soccer? |
| It | It plays soccer. | It does not play soccer. | Does it play soccer? |
This table uses the sentence “I play soccer” as a base for illustrating positive, negative, and question sentences in the Present tense.
Let’s explore the uses of the present tense for the given scenarios:
Habits (Present)
General Truths (Present)
Repeated Actions or Events (Present)
Fixed Arrangements/Timetables (Present)
Feelings/Opinions/Beliefs (Present)
Examples:
Instructions (Present)
To get the Simple Present Tense, we need to know what “third person” means first.
Third person singular
In the third person singular (he/she/it), the addition of an “-s” to the verb is a standard practice, but there are a few rules to follow:
The present Continuous is sometimes called the present progressive; however, as most textbooks refer to it as the continuous, I will use that term here.
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I am eating. | I am not eating. | Am I eating? |
| You | You are eating. | You are not eating. | Are you eating? |
| We | We are eating. | We are not eating. | Are we eating? |
| They | They are eating. | They are not eating. | Are they eating? |
| He | He is eating. | He is not eating. | Is he eating? |
| She | She is eating. | She is not eating. | Is she eating? |
| It | It is eating. | It is not eating. | Is it eating? |
This table is based on the sentence “I am eating,” demonstrating the positive, negative, and question forms in the Present Continuous tense for various pronouns.
Let’s focus on the examples that involve the present continuous tense:
Actions happening in the moment (Present Continuous):
Temporary events (Present Continuous):
To complain or emphasize continuous behavior with words like ‘always’, ‘forever’, and ‘constantly’ (Present Continuous):
Examples:
The next present tense is the present perfect. As highlighted in the main verb tense table above, it is constructed with have or has and the past participle form of the verb.
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I have completed the project. | I have not completed the project. | Have I completed the project? |
| You | You have completed the project. | You have not completed the project. | Have you completed the project? |
| We | We have completed the project. | We have not completed the project. | Have we completed the project? |
| They | They have completed the project. | They have not completed the project. | Have they completed the project? |
| He | He has completed the project. | He has not completed the project. | Has he completed the project? |
| She | She has completed the project. | She has not completed the project. | Has she completed the project? |
| It | It has completed the project. | It has not completed the project. | Has it completed the project? |
This table now uses the sentence “They have completed the project” as a base for illustrating positive, negative, and question forms in the present perfect tense.
Let’s elaborate on each of the uses of the present perfect with examples:
Actions that start in the past and continue to the present:
Life experiences, at an unspecified time in the past:
Repeated action in an unspecified period:
Unfinished time (today, this week, this month, this year):
A finished action with a present result:
Recent past with the words ‘just’, ‘recently’, ‘already’, and ‘yet’:
Examples:
As implied by its name, this tense incorporates features from both the perfect and continuous tenses. Specifically, it combines have or has with the past participle been, followed by the verb+ing.
In any of the tenses, you can form positive, negative, or interrogative (a question) sentences.
| Person | Positive | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I have been working since morning. | I have not been working since yesterday. | Have I been working since last week? |
| You | You have been exercising for an hour. | You have not been exercising for days. | Have you been exercising since yesterday? |
| We | We have been learning since the semester started. | We have not been learning for a long time. | Have we been learning for weeks? |
| They | They have been practicing for the competition. | They have not been practicing since the event began. | Have they been practicing since the last meeting? |
| He/She/It | He has been reading since he woke up. | He has not been reading for a while. | Has he been reading for hours? |
| It | It has been growing for months. | It has not been growing since it was planted. | Has it been growing since last summer? |
Let’s explore the uses of the present perfect continuous tense for the given scenarios:
Actions that started in the past and continue in the present:
Example:
To emphasize the duration or ‘how long’ (with for and since):
Examples:
Recently finished actions with present results:
Example:
Answers:
1. What are the different present tenses?
2. At what times should I utilize the present tense?
3. How is the present continuous tense formed?
4. In what situations do I use the present continuous tense ?
5. How do I form the present perfect tense ?
6. How is the present perfect continuous tense formed?
Get Printable Worksheets on English Tenses and Check Your Understanding